costs from $250
products
Syringe Injection System
Syringe injection is the most common and arguably the most reproducible method of headspace sampling. It is illustrated in the figure below.
The syringe is heated and agitated in an oven for a pre-defined period of time (step 1). The heated syringe then removes an aliquot of the headspace (step 2) and injects it directly into the GC (step 3).
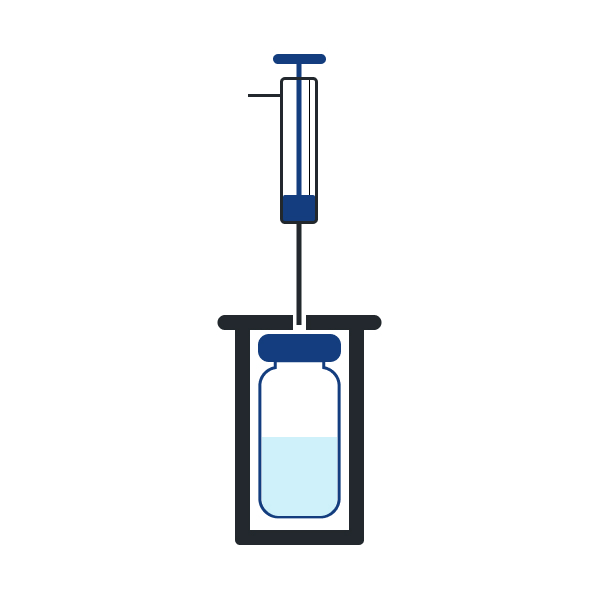
Step 1
Sample reaches equilibrium
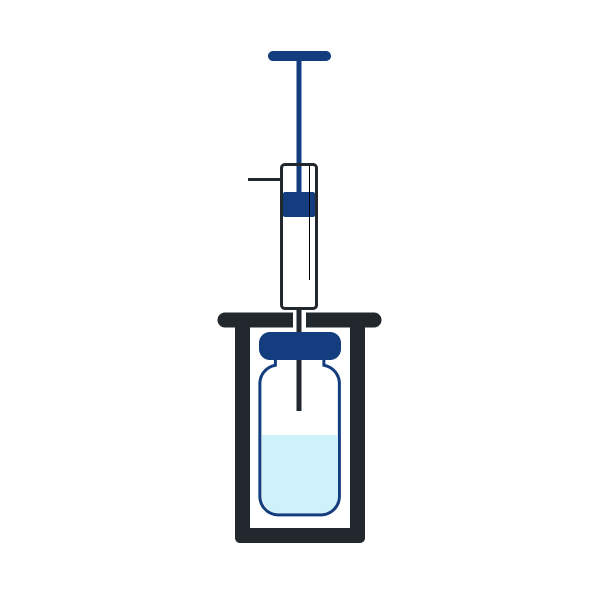
Step 2
Sample is extracted from the headspace
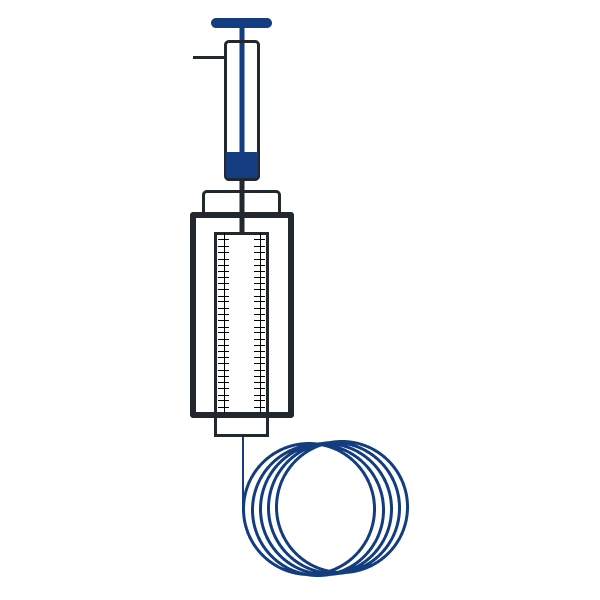
Step 3
Sample is injected
The syringe must be heated above the temperature of the oven to avoid the risk of condensation and hence carry-over from one sample to the next. After injection, the syringe is flushed with nitrogen or other inert gas.
Advantages of a Syringe Injection System
There are several advantages of this type of system:
- Very high level of reproducibility
- Low carry-over
- Fast transfer of sample to GC
- Precise control of sample syringe for sample size and injection speed
- Easy to clean syringe
- GC injection port is always free for manual samples
Many syringe autosamplers can be retrofitted onto existing GC systems. The Manual Headspace Sampler is GC-independent and is a simple syringe injection system.