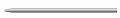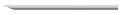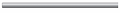Selection guide for GC syringes – needle tips
Syringes are of great importance in the operation of GC systems, since the sample is poured in through them from the sample bottle into the inlet. When using syringes, different sources of error can falsify the result. The reason for this is primarily the large selection of inlets from various manufacturers as well as the variety of autosamplers. The following table helps to counteract this problem by opposing possible needle shapes and their corresponding applications.
| Needle Tip | Application |
|---|---|
| Conical Tip |
|
| Bevel Tip
|
|
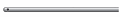
| Side Hole Tip
|
|
| LC Tip
|
|
| Dual Gauge
|
|
Connection of the needle tip
In addition to the selection of a suitable needle tip for the respective application, the connection of the needle to the injection body can also be varied. A distinction is made between fixed needles, interchangeable needles and injection needles with a luer connection. The characteristics of the respective needle types can be found in the table below.
| Tip Connection | Application |
|---|---|
| Solid Needle
|
|
| Disposable Needle
|
|
| Luer Connection
|
|
Selection guide for syringe plungers
The materials for the production of syringe plungers are divided into metals (stainless steel, titanium/nickel alloys, etc.) and synthetics (PP, PTFE, etc.). Apart from the material, different types of plungers are distinguished as well. The most frequently applied plunger types as well as their application areas are summarized in the following table.
| Plunger Type | Application |
|---|---|
| Standard Plunger (Metal)
|
|
| Gas-tight Plunger (PTFE Tipped)
|
|
| Plunger-in-needle (micro volume)
|
|
| Plunger Protection
|
|
| Guided Plunger
|
|
| SuperfleX™ Plunger
|
|